How to manually update packages for Digital Gardens
Reminder: Free software isn't free. Support Ole, the Digital Garden developer: Buy Ole Eskild Steensen a Coffee - oleeskild - Ko-fi
tl;dr: Steps to manually update a package dependency
- Download GitHub Desktop and an IDE like Visual Studio Code or Kate
- Install Node.js
- Prebuilt Installer (Windows/Mac)
- Package Manager (Linux)
- Also note, on Kubuntu, I was able to install NPM with
sudo apt install npmand used Kate as my IDE, and it worked fine.
- Also note, on Kubuntu, I was able to install NPM with
- Clone your repository to GitHub Desktop and open the repository in your editor.
- Edit the
packages-lock.jsonfile with the patched version, save the file, then runnpm audit fix- If packages need a specific version of Node installed, you can run
nvm install --latest-npm(or the version you want) to download and install the latest version of Node, thennvm use [version of node]
- If packages need a specific version of Node installed, you can run
- In GitHub Desktop, Commit to main, then Push origin
Finding the Answer
I use Digital Garden to publish my Obsidian notes, and I recently noticed an outstanding CVE for the plugin.
Just pop into your GitHub and check the Security tab, and check out what Dependabot found but couldn't repair automatically!
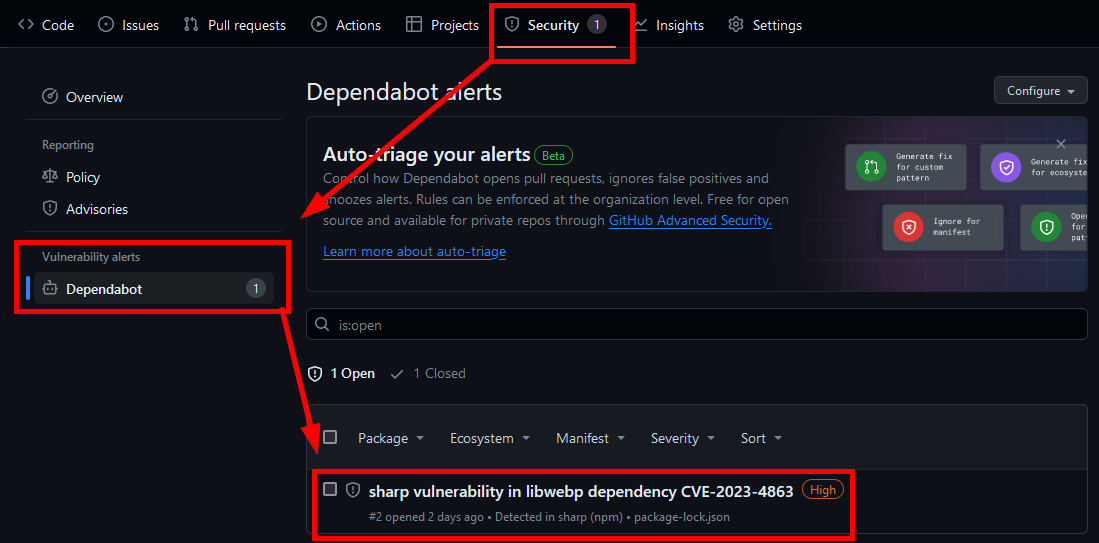

So, how do we fix this?
In the second screenshot, we can see a bit of code, a dependency, and now we just need to find it.
Download GitHub Desktop, login, clone your repository, and open it in Visual Studio Code. If you've already logged in and installed GitHub and need to do this for another Repo, you can follow the steps in the screenshot below:

If you don't see Visual Studio here but have it installed, you can go to File>Options>Integrations and select it from there.
And now in Visual Studio, we see all of our files; great. Now what?
Well, we've got two files at the very top that are important to know about; package.json and package-lock.json.
To put it shortly, package.json is manually configured and lists all the dependencies the app requires, and package-lock.json is automatically created when you run npm install.[1]
To work with Java, we need to install Node.js, and the best way to install Node.js is to install NVM.[2]
So lets' try this first.
I open a Terminal by going to Terminal>New Terminal, and then run npm install, and here's what I get.
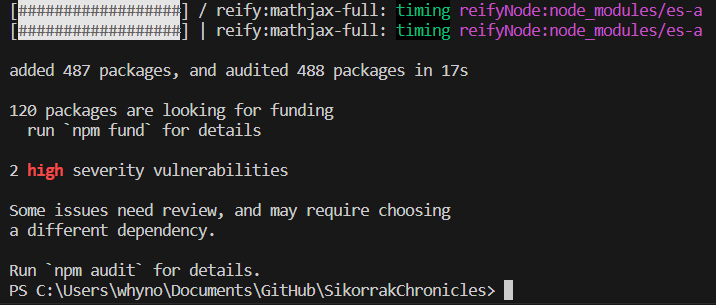
Wow, TWO high severity vulnerabilities? Jackpot!
Let's try npm audit fix, that works sometimes.

Damn, that didn't work.
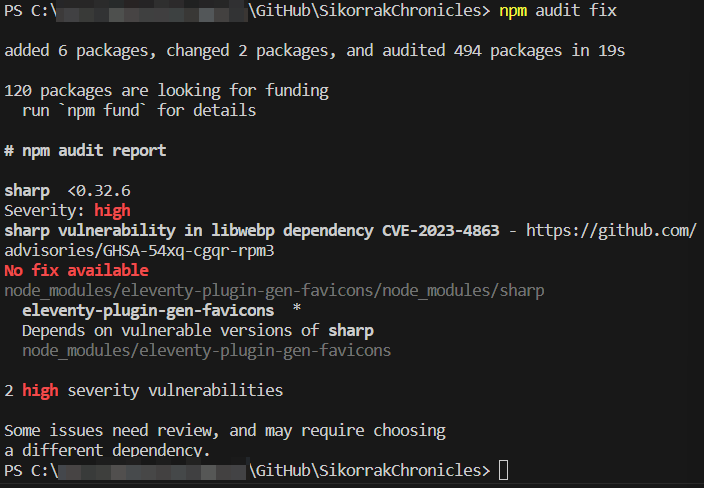
Let's try to fix it manually; it's a sharp vulnerability, which is required for eleventy-plugin-gen-favicons; we can search for either of those terms in package-lock.json until we find the dependency we're looking for, which is this:
"node_modules/eleventy-plugin-gen-favicons": {
"version": "1.1.2",
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/eleventy-plugin-gen-favicons/-/eleventy-plugin-gen-favicons-1.1.2.tgz",
"integrity": "sha512-DtxS3J+ujDVZ9oP5RTOTxwET2K7S7WEvQ7XE/S3TwM7uQR/NOqHibuZXyftutK22EU1UInQc2yP1JZ7mtnWJUQ==",
"dependencies": {
"fast-deep-equal": "^3.1.3",
"png-to-ico": "^2.1.8",
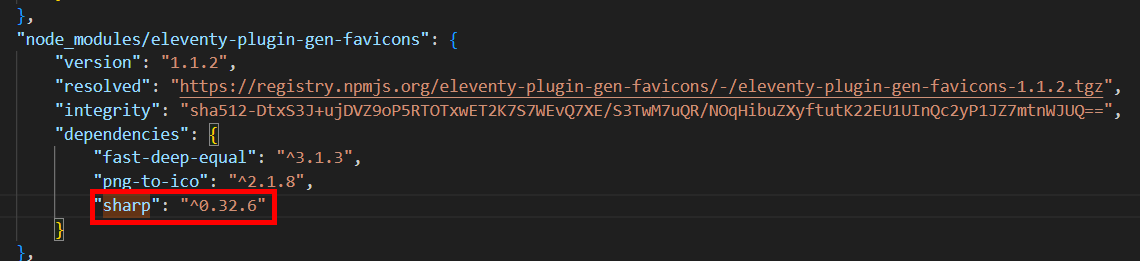
"sharp": "^0.31.3"
}
},
We can see that the Sharp version required is "^0.31.3", and it's weird as heck that it's not updating to 0.32.6, since it's theoretically a Minor version update[3]
Max from the future: I'm not a developer, but I think you can also run
npm update, followed bynpm audit fix, to automatically update all your packages. It hasn't broken any of my sites so far!
Well, let's just manually fix this then. Change the sharp version to match the latest safe version and hit save.
Once saved, I'll run npm audit fix again in the terminal, and...
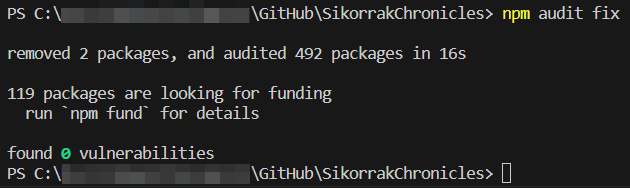
Zing!
Now all we have to do is commit the changes in GitHub Desktop. When you open GitHub Desktop, you'll see all the changes being made on the right, and all the files that were changed on the left.
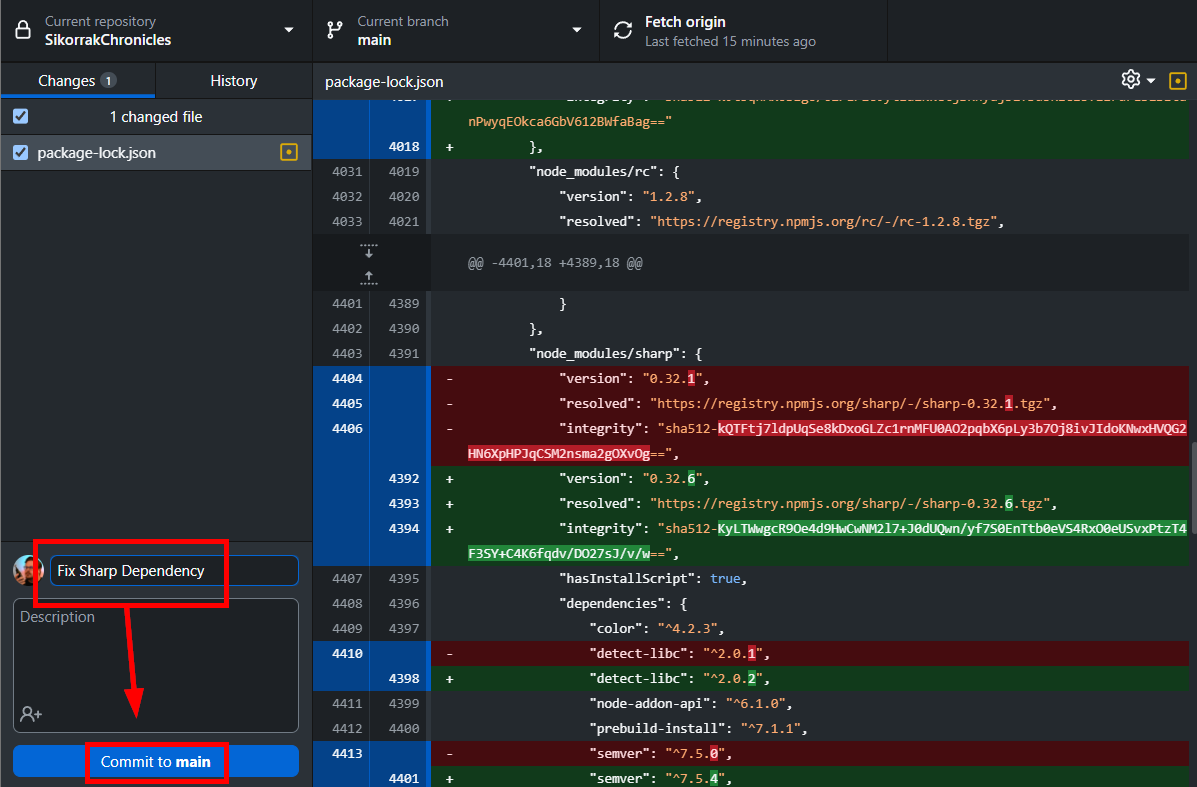
Enter a reasonable description for the changes at the bottom left, then it "Commit to main", and finally "Push origin"
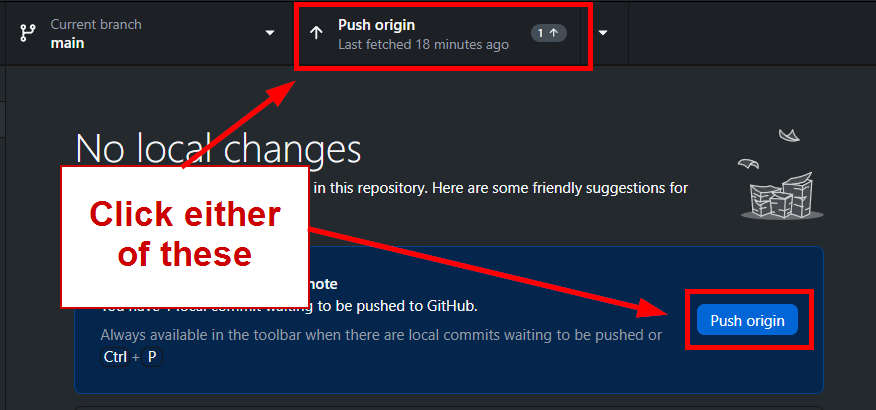
Make sure you are committing to main, otherwise you're just updating a branch and it won't reflect on your site.
Refresh the GitHub page, and we're in the clear; no more known vulnerabilities.
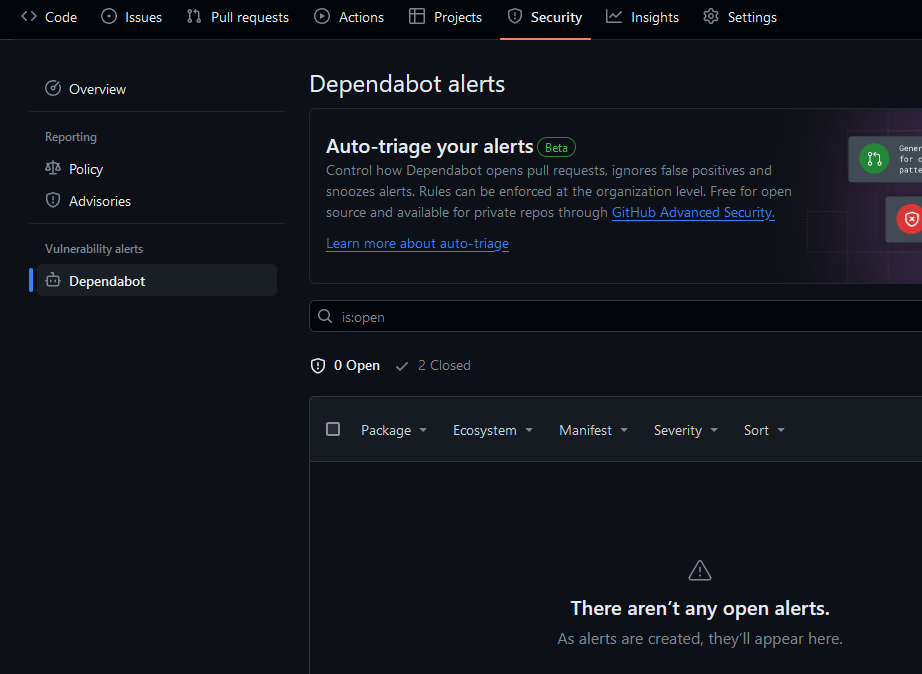
And with no small degree of luck, our site is still online. Success!
Troubleshooting
If you finish this process and your builds start failing, don't worry; there are a couple of things that might have caused it, and a few ways we can fix them.
As a reminder, here are the steps you should have followed when manually updating your packages:
Problems and Solutions - Manual Package Updates
- Builds start failing
- Possible cause:
- You changed the package version without then running
npm audit fixto update the rest of the dependencies inpackage-lock.json.
- You changed the package version without then running
- Possible solution:
- Revert changes and go back through the steps
- Possible cause:
npm audit fixis still detecting vulnerabilities after updating the package version- Possible cause:
- You Probably didn't save the changes you made to
package-lock.jsonbefore you rannmp audit fixnpm audit fixmakes and saves changes to the file, so if you haven't saved your changes, then there's going to be overlap that Visual Studio Code is going to be upset about
- You Probably didn't save the changes you made to
- Possible solutions:
- Close the file in your editor, discarding changes. Reopen the file, edit the package version, and then re-run
npm audit fix. - Close your editor entirely, return to GitHub Desktop, right-click the pending changes and select "Discard changes." Then go through the steps again in the tl;dr, making sure to save the file before running
npm audit fix
- Close the file in your editor, discarding changes. Reopen the file, edit the package version, and then re-run
- Possible cause:
Revert Changes
If you're in panic mode and the site is fully down, sometimes it's better to just hit "undo," and it's easy to do with GitHub Desktop.
Click on the History tab below Current Repository at the top right, right-click the commit you want to undo, and select Revert changes in commit. When ready, click Push Origin to send the changes to GitHub.[4]
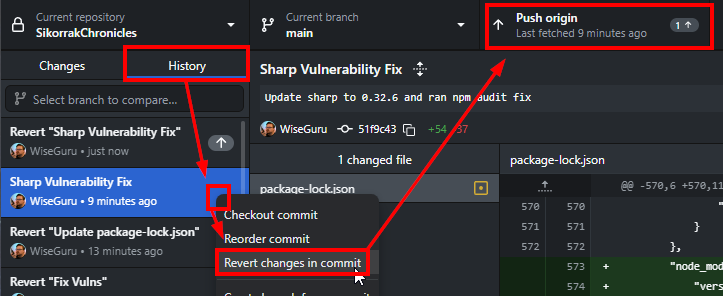
What's great here too is that you can view ALL commits made to your repository, not just the ones you made on your computer. Convenient!
For reference: Package.json vs Package-lock.json ↩︎
A caret is supposed to update minor versions update automatically Package.json vs Package-lock.json ↩︎
If you do this by accident and want to cancel the revert, just right click the commit titled 'Revert "(commit being undone)"', select "Undo changes", then under the Changes tab, right click the changes being made and select "Discard changes..." ↩︎